Some suggestions for improving mysql database security

MySQL is the most popular RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) relational database management system. It was developed by the Swedish MySQL AB company and eventually acquired by Oracle. Later, a number of open source branches appeared one after another,the more popular ones being XtraDB, Percona, MariaDB (The main creator of MariaDB is Monty Widenius,Who is also the original creator of MySQL). MySQL and the open source version are both popular relational OLTP databases, helping users solve OLTP-related problems in countless enterprises, so how to How to improve the security of MySQL itself?This article will lead you to do a good job of MySQL security.
Upgrade the operating system
The first step in improving MySQL security is to upgrade the operating system of the server where MySQL is located. The operating system itself will have security vulnerabilities and other problems, and the operating system suppliers will also regularly release upgrade patches, so in order to avoid security risks caused by system vulnerabilities , we must regularly upgrade the operating system kernel and patches. We need to consider the compatibility of the patch version, do a good job of all database-related backups, and make multiple sets of plans in advance, and we need to test the database with the kernel and the same version of the database server first. Patch verification, then be sure to implement relevant stress tests and carefully analyze whether the system vulnerability has been fixed, verify the difference between before and after the upgrade, and then gradually upgrade to the database machine system in the production environment to avoid major security incidents in the company. Now, DB and operation and maintenance can basically start running, and developers can update their resumes, ready to start a new life (😄)…

Upgrade MySQL
MySQL products are constantly evolving, the community is constantly feeding back problems, and the community team has been fixing various problems found in the testing process, so in order to ensure that your MySQL has always been safe and reliable, the best way is to regularly repair or upgrade MySQL Kernel patches and related plug-in patches can avoid major vulnerabilities or hidden dangers in MySQL itself, which will bring irreparable losses to the company’s performance.

Upgrading MySQL Dependent Components
In addition to its own software, MySQL also includes a lot of dependent software, such as Innodb, Password components, Replication components, Auth components, etc. Similar to the operating systems mentioned above, these softwares themselves also have potential security risks. In order to ensure the security of the entire MySQL system, it is recommended that you upgrade the version of the MySQL-dependent software. Of course, you must also pay attention to the compatibility of the version of the dependent software, and pay attention to the instructions on the relevant patch upgrades released by the MySQL official website or the community.
Security Components of Operating Systems
The operating system itself also has a variety of security components, such as firewalls in Windows, security policies (local policies, domain policies, OU policies), Defender anti-spyware, Action Center (action center and problem diagnosis reminder function), and Linux such as CentOS itself It includes Firewalld (Iptables firewall), Selinux (mandatory access control), AIDE (advanced intrusion detection environment), ACL (file permissions of R\W\X) to provide security capabilities, so be sure to configure related software when deploying related software Component security level and system granularity policy, it is best not to turn off the Iptables firewall and Selinux in the MySQL server. Of course, when Iptables is turned on, more attention needs to be paid to the operation and maintenance management. It is necessary to open several ports used by MySQL and the ports required by the application, and all others must be closed or prohibited.

Improve password complexity
Password settings should be as complicated as possible, and must not be leaked and need to be changed frequently, such as operating system passwords and various other software access passwords. Here we only talk about the MySQL password enhancement plug-in, and validate_password is a new password verification plug-in that can be introduced after mysql5.6. , to manage the length and strength of user passwords, and the related parameters are set more strictly. When this plugin is used, it will check whether the set password conforms to the currently set strength rules. If not, the setting will be rejected. The relevant parameters are mainly judged by the parameters at the beginning of mysql> show variables like ‘validate%’;, how to configure it, and search for the relevant parameters. Blog, the main parameters are as follows:
1. validate_password_policy
#Password Policy(0 or LOW\1 or MEDIUM\2 or STRONG )
2.validate_password_length
#Used to set the minimum length of the password, the default value is 8, the minimum is 0
3. validate_password_mixed_case_count
#When validate_password_policy is set to MEDIUM or STRONG, the number of lowercase and uppercase letters in the password at least, the default is 1 and the minimum is 0; the default is at least one lowercase and one uppercase letter
4.validate_password_number_count
# When validate_password_policy is set to MEDIUM or STRONG, the number of digits at least in the password, the default is 1 and the minimum is 0
5. validate_password_special_char_count
# When validate_password_policy is set to MEDIUM or STRONG, the minimum number of special characters in the password, the default is 1 and the minimum is 0
Password Complexity Rules:
- Numbers, uppercase letters, lowercase letters, special symbols, 4 categories at least choose 3 categories
- The length of the password should be as long as possible, generally greater than 7 digits
- It’s better to use random strings, don’t use Yung Kee strings
- Regularly change passwords, usually two months
- The cycle period of the password should be large, for example, your password replacement cannot use the most recently used password
Password length cracking difficulty (scientists from Georgia Institute of Technology in the United States said that if a 12-bit password (multiple characters: numbers + uppercase and lowercase letters + special characters) is used, with the current technical level, it will take hackers 17134 years to crack).
If you use a 12-bit password (researchers still recommend 12-bit passwords), then all use numbers, then the complexity is 10 to the 12th power.
If numbers and lowercase letters are used, the complexity is 10 digits plus 26 lowercase letters to the 12th power, which is 36 to the 12th power.
If you use numbers, lowercase letters, uppercase letters, then the complexity is 10 digits plus 26 lowercase letters plus 26 uppercase letters, which is 62 to the 12th power.
Use SSL Protocol
Needless to say, there are many benefits of SSL. If the database needs external access, and the external I am talking about is from the public network, then I strongly recommend that you apply for an SSL certificate, then deploy the ssl certificate, close the HTTP access method, and let Everyone accesses the MySQL database through the HTTPS protocol. If it is an intranet, it is not necessary. You can control security in other aspects, because enabling SSL requests and enabling ssl encrypted connections will inevitably reduce performance, and the performance overhead is about 25% (online I mean, I haven’t actually tested it).

Principle of least privilege
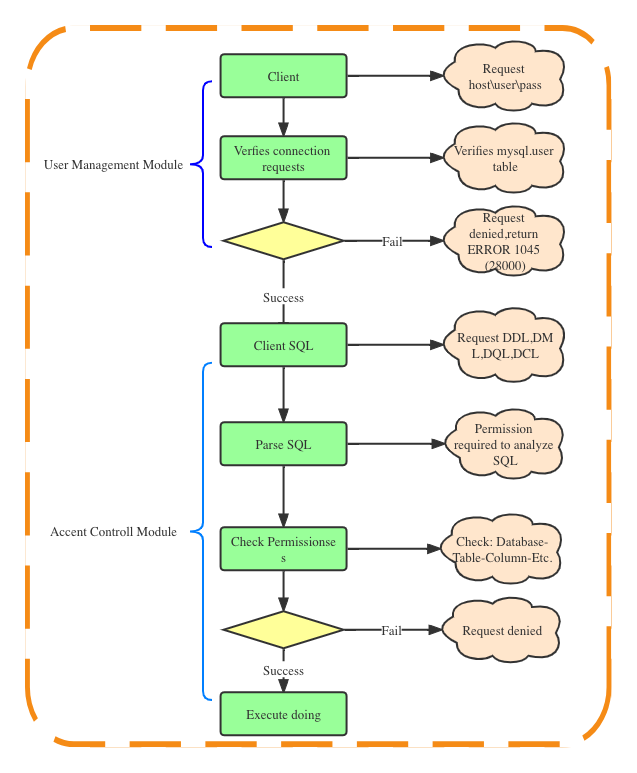
MySQL authorized users should abide by the principle of minimizing permissions from beginning to end. MySQL permissions are divided into several levels, host authorization->user authorization->database authorization-table authorization-column authorization-other operations (such as stored procedures, master-slave replication) , function execution), etc., generally speaking, there are 6 levels. Therefore, when authorizing, you must strictly control the corresponding permission level, and do not set too large (boundary exceeded, risky) or too small (restrict business operations). Required Strictly control the management of OS and DB accounts to prevent account information from leaking, especially for root and mysql accounts, and access authorization limits access to host information. We can limit the range of visiting hosts by specifying the host name, domain name or IP address information of the host during authorization. These accounts will bring great security risks to the system, so we must delete them as soon as possible before they are officially activated, or Set a relatively secure password. To authorize a user, use the GRANT command, and to remove a user’s existing permissions, use the REVOKE command. Of course, in addition to these two commands, there is also a more violent method, which is to update the system tables directly, both in mysql(user(proxies_priv)\db\tables_priv\columns_priv\procs_priv) and information_schema(USER_PRIVILEGES\SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES\TABLE_PRIVILEGES\COLUMN_PRIVILEGES) under the two internal libraries, 90% of the permission-related tables under different libraries overlap, MySQL’s access control is actually composed of two functional modules, one is the user responsible for “guarding the MySQL gate” The management module, the other is the access control module responsible for monitoring every action of the visitor.
Authorization follows principles
The basic basis of MySQL authorization is the target responsibility, and the authority is the target responsibility that the user needs to assume. Do not authorize too much or insufficient, just meet the actual business. Therefore, the following principles should be followed when authorizing
- Minimum principle: that is, only the power to make decisions or deal with a certain problem is granted, and the power will be withdrawn after the problem is solved
- Conditional authorization: that is, only under a certain environmental condition, grant a certain power to the subordinate, and the environmental conditions change, the authority should also change accordingly
- Timing authorization: that is, a certain power granted to subordinates has a certain time limit, and the expired power should be withdrawn
- Authorization transfer: A very important feature in the MySQL database is the transfer of permissions. If the WITH GRANT OPTION parameter is not added when authorizing the user, the permissions cannot be transferred.
- Operation track: It is necessary to issue authorization through some system management platforms, so that you can know who and when to grant which permissions to which resources to operate which resources, and then which user operates when and in what way A detailed log archive is required for any resource to be operated.
- Regular review: It means that the account administrator needs to regularly check whether the log is abnormal, or check whether some accounts are no longer used, and clear them immediately to avoid subsequent accidents.

Security Audit Log
Now data is money, to prevent data leakage, to find out where the source of the leak came from as soon as possible, you must need relevant log records, otherwise there will be breaking news in the technology circle, a certain company has data leakage, or the database is dragged However, the company came out to clarify, we are continuing to investigate, and we have not said who leaked what content through some method (because there is no log, it will not be able to answer for a while), which will have a fatal blow to the company’s market. ,Database auditing can record database activities on the network in real time, conduct fine-grained audit compliance management for database operations, warn the risk behaviors suffered by the database, and block attack behaviors. It records, analyzes and reports the user’s access to the database to help users generate compliance reports and trace the source of accidents.

Data Backup Policy
Data security is now the core competitiveness of enterprises or enterprises, and the scale of data in various industries is growing at the terabyte level. How to ensure the integrity, availability and confidentiality of network data, and not be affected by the security threats of information leakage and illegal tampering, has become a government agency. The core issues to be considered in the healthy development of the informatization of public institutions. MySQL data security backup has the following types:
Divide by method according to backup type
- Hot Backup: Hot backup is online backup, which has no impact on the running database operation, that is, the business is imperceptible, also known as online backup.
- Cold Backup (cold backup): Cold backup is just the opposite of hot backup. It needs to be operated when the database is stopped. Generally, the business can accept the shutdown request. This is also the safest backup operation.
- Warm Backup: Warm backup is between hot backup and cold backup, which will affect the current database operation, and ensure the consistency of backup data through some locks or current limiting or reducing business performance.
Divide according to the content of the backup file
- Logical backup: Logical backup is that the content is readable, such as exporting SQL or xls files, etc.
- File backup: directly copy the relevant files in the Mysql data directory (frm\ibdata\mysql-bin.000\mysql-bin.index) or back up the entire MySQL data directory
According to the content of the backup data
- Full backup: A full backup is a complete backup of the database. Generally, a full backup is performed before the first backup or incremental backup.
- Incremental backup: backup on the basis of full backup, you can set the time to every minute\hour\day\week, etc.
- Log backup: Log backup is a backup that uses MySQL’s (Replication) principle to realize asynchronous real-time synchronization of binary logs to the slave database for redoing.
According to the area of backup data
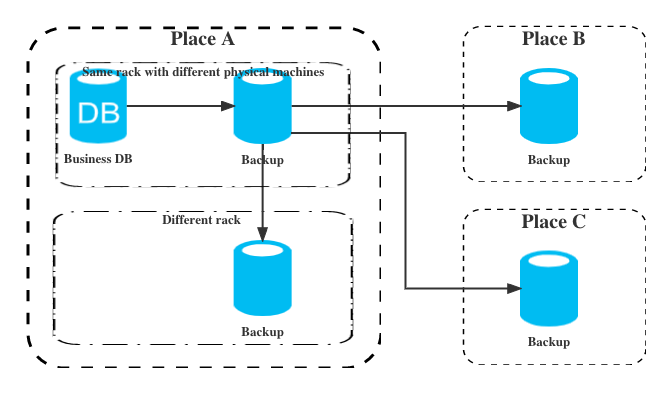
- Same computer room strategy: that is, the database machine to be backed up cannot be on the same device as the database machine to be backed up, to prevent system problems or hardware problems of the current hardware equipment, etc.
- Cross-machine room strategy: also known as dual-machine remote hot backup, that is, the database machine to be backed up cannot be in the same machine room as the database machine to be backed up, it is best to do three backup tests, such as one in the machine room and two across the machine room.